Sistema Contable en Azure con Terraform
Este proyecto implementa la infraestructura para un sistema contable en Azure utilizando Terraform. La arquitectura está diseñada para ser segura, escalable y fácil de mantener.
Estructura del proyecto
├── main.tf
├── network.tf
├── database.tf
├── security.tf
├── storage.tf
├── webapp.tf
├── variables.tf
└── README.mdEl proyecto está organizado en varios archivos .tf, cada uno con un propósito específico:
main.tf: Configuración del proveedor y grupo de recursosnetwork.tf: Configuración de la red virtual y subnetsdatabase.tf: Configuración del servidor SQL y base de datossecurity.tf: Reglas de seguridad y NSGstorage.tf: Configuración de la cuenta de almacenamientowebapp.tf: Configuración del App Service y Web Appvariables.tf: Definición de variables
Componentes Principales
1. Proveedor y Grupo de Recursos (main.tf)
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
subscription_id = var.subscription_id # ID de suscripción de Azure
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = "rg-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
location = var.location
tags = var.tags
}En este archivo, configuramos el proveedor de Azure y creamos el grupo de recursos base para nuestro proyecto.
2. Red Virtual y Subnets (network.tf)
Vnet
Subnets
Creamos una red virtual con tres subnets:
- Web: Para la capa de presentación
- App: Para la lógica de negocio
- Data: Para almacenar datos de forma segura
3. Base de Datos SQL (database.tf)
resource "azurerm_mssql_server" "sqlserver" {
name = "sql-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
version = "12.0"
administrator_login = var.sql_admin_login
administrator_login_password = var.sql_admin_password
tags = var.tags
}
resource "azurerm_mssql_database" "sqldb" {
name = "sqldb-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
server_id = azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver.id
collation = "SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS"
license_type = "LicenseIncluded"
max_size_gb = 2
sku_name = "S0"
tags = var.tags
}
resource "azurerm_private_endpoint" "sql_pe" {
name = "pe-sql-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets["data"].id
private_service_connection {
name = "psc-sql-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
private_connection_resource_id = azurerm_mssql_server.sqlserver.id
is_manual_connection = false
subresource_names = ["sqlServer"]
}
tags = var.tags
}Configuramos un servidor SQL de Azure y una base de datos, utilizando un Private Endpoint para garantizar un acceso seguro.
4. Seguridad (security.tf)
resource "azurerm_network_security_rule" "allow_https" {
name = "AllowHTTPS"
priority = 100
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_range = "443"
source_address_prefix = "*"
destination_address_prefix = "*"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
network_security_group_name = azurerm_network_security_group.nsg.name
}
resource "azurerm_network_security_rule" "allow_sql" {
name = "AllowSQL"
priority = 200
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_range = "1433"
source_address_prefix = azurerm_subnet.subnets["app"].address_prefixes[0]
destination_address_prefix = "*"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
network_security_group_name = azurerm_network_security_group.nsg.name
}Definimos reglas de seguridad en nuestro Network Security Group, incluyendo:
- Permitir tráfico HTTPS
- Permitir acceso SQL desde la subnet de aplicaciones
5. Almacenamiento (storage.tf)
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "storage" {
name = "st${var.project}${var.environment}"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
account_tier = "Standard"
account_replication_type = "LRS"
tags = var.tags
}
resource "azurerm_storage_container" "container" {
name = "documents"
storage_account_name = azurerm_storage_account.storage.name
container_access_type = "private"
}
resource "azurerm_private_endpoint" "storage_pe" {
name = "pe-storage-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets["data"].id
private_service_connection {
name = "psc-storage-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
private_connection_resource_id = azurerm_storage_account.storage.id
is_manual_connection = false
subresource_names = ["blob"]
}
tags = var.tags
}Creamos una cuenta de almacenamiento con un contenedor privado para documentos, implementando un Private Endpoint para acceso seguro.
6. Aplicación Web (webapp.tf)
resource "azurerm_service_plan" "plan" {
name = "asp-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
os_type = "Linux"
sku_name = var.app_service_sku
tags = var.tags
}
resource "azurerm_linux_web_app" "webapp" {
name = "app-${var.project}-${var.environment}"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
service_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.plan.id
site_config {
application_stack {
php_version = "8.0" // Cambiar de lengaje si es necesario
}
always_on = true
vnet_route_all_enabled = true
}
tags = var.tags
}
resource "azurerm_app_service_virtual_network_swift_connection" "vnet_integration" {
app_service_id = azurerm_linux_web_app.webapp.id
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets["web"].id
}Configuramos un App Service Plan y una Web App PHP, integrándola con nuestra red virtual para una comunicación segura.
7. Variables (variables.tf)
variable "project" {
description = "Project name"
default = "contable"
}
variable "environment" {
description = "Environment (dev, staging, prod)"
default = "dev"
}
variable "location" {
description = "Azure region"
default = "East US 2"
}
variable "tags" {
description = "Tags to apply to resources"
type = map(string)
default = {
project = "sistema-contable"
environment = "dev"
managed_by = "terraform"
}
}
variable "vnet_address_space" {
description = "Address space for the VNet"
default = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
}
variable "subnet_prefixes" {
description = "Address prefixes for subnets"
type = map(string)
default = {
web = "10.0.1.0/24"
app = "10.0.2.0/24"
data = "10.0.3.0/24"
}
}
variable "app_service_sku" {
description = "SKU for App Service Plan"
default = "S1"
}
variable "sql_admin_login" {
description = "Admin username for SQL Server"
default = "sqladmin"
}
variable "sql_admin_password" {
description = "Admin password for SQL Server"
sensitive = true
}
variable "subscription_id" {
description = "ID de suscripción de Azure"
type = string
}Definimos variables para hacer nuestro código más flexible y fácil de personalizar, incluyendo:
- Nombre del proyecto
- Entorno (dev, staging, prod)
- Región de Azure
- Configuraciones de red
- SKU del App Service
Despliegue
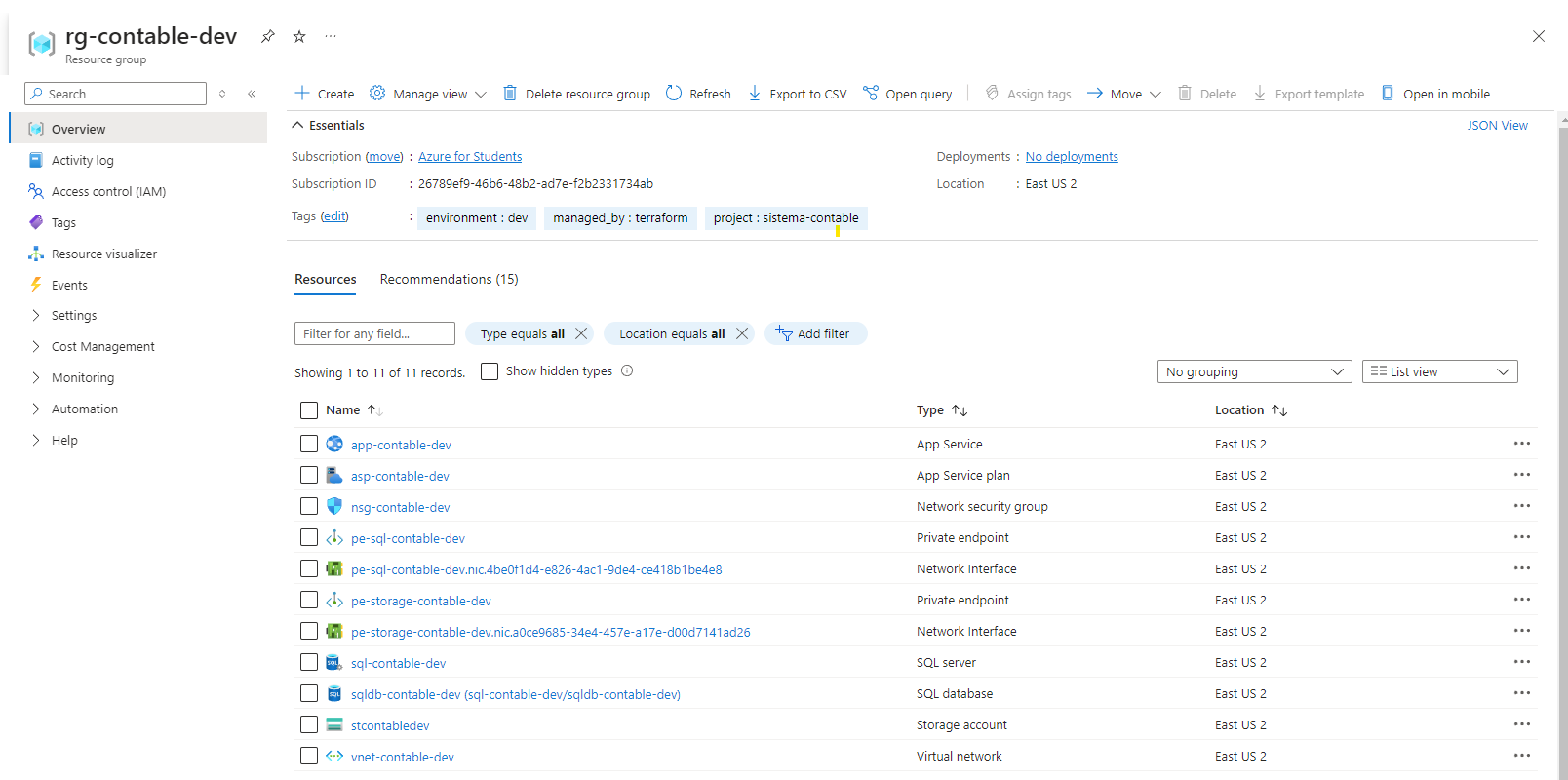
Para desplegar esta infraestructura:
-
Clona este repositorio
-
Actualiza las variables en
variables.tfsegún tus necesidades -
Ejecuta:
terraform init terraform plan terraform apply
Arquitectura Final
Este diagrama muestra cómo todos los componentes se conectan entre sí, proporcionando una visión general de la infraestructura desplegada.
Seguridad
Este proyecto implementa varias medidas de seguridad:
- Uso de Private Endpoints para SQL y Storage
- Network Security Group con reglas específicas
- Segregación de redes mediante subnets